Mobile Device Acquisition: Logical vs Physical vs Cloud Extraction Explained
Mobile device acquisition methods are used in digital forensics to collect data from smartphones and other mobile devices. There are three main types of extraction methods: logical, physical, and cloud.
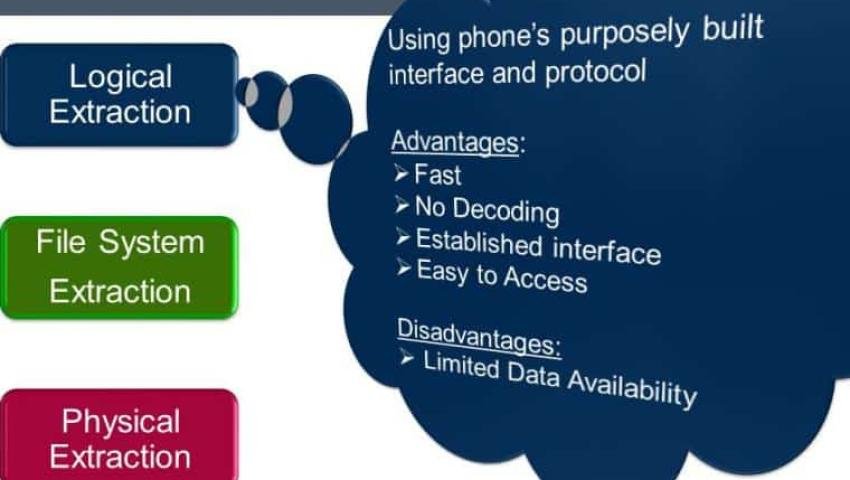
Logical Extraction
A logical extraction is a quick and simple method that copies all the user-accessible data from a device. This is done by communicating with the device's operating system (OS) using a software tool. It's similar to backing up a phone, but with a forensic tool that preserves data integrity.
- What it collects: Call logs, text messages, contacts, calendar entries, photos, and videos that are visible to the user.
- Pros: It's a fast, non-intrusive method that is generally safe for the device. It is often a good first step in an investigation.
- Cons: It cannot recover deleted data or access hidden files, such as system logs or app data that isn't stored in a standard location. It also may not work on locked devices unless a trusted computer is available.
Physical Extraction
A physical extraction is a more complex and thorough method that creates a bit-by-bit copy of the device's internal memory. This is the most comprehensive type of data acquisition, as it can access all data on the device, including hidden and deleted information.
- What it collects: All data on the device, including deleted files, file fragments, and data from unallocated space. It provides a complete picture of the device's contents.
- Pros: Provides the most complete dataset and can recover evidence that is no longer visible to the user. It is the most forensically sound method.
- Cons: It's a much slower process and requires more specialized tools and expertise. It may not work on all modern, highly-encrypted devices, as security features like File-Based Encryption (FBE) can make this method difficult.
Cloud Extraction
Cloud extraction involves acquiring data that a mobile device has backed up to a cloud service. This method does not require direct access to the physical device. Instead, forensic tools use login credentials to access and download data from the cloud storage.
- What it collects: Data that has been synchronized with a cloud service, such as photos, documents, contacts, and application data (e.g., from messengers or social media apps).
- Pros: This method can be used even if the physical device is damaged, lost, or inaccessible.
- Cons: The amount of data retrieved is limited to what the user has chosen to back up to the cloud. It is dependent on the cloud service provider's security and data retention policies.
Mrityunjay Singh
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *